function
What is serverless
Serverless computing is a method of providing backend services on an as-used basis. A serverless provider allows users to write and deploy code without the hassle of worrying about the underlying infrastructure. code executes in a fully managed environment and no need to provision any infrastructure.
Introduction to cloud functions
Google Cloud Functions is a serverless execution environment for building and connecting cloud services. With Cloud Functions you write simple, single-purpose functions that are attached to events emitted from your cloud infrastructure and services. Your Cloud Function is triggered when an event being watched is fired. Your code executes in a fully managed environment. There is no need to provision any infrastructure or worry about managing any servers.
Functions Framework
The Functions Framework lets you write lightweight functions that run in many different environments. Functions framework
package main
import (
"github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/functions-framework-go/funcframework"
p "github.com/cloudmock"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
if err := funcframework.RegisterHTTPFunctionContext(ctx, "/", p.GoMock); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("funcframework.RegisterHTTPFunctionContext: %v\n", err)
}
port := "8080"
if envPort := os.Getenv("PORT"); envPort != "" {
port = envPort
}
if err := funcframework.Start(port); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("funcframework.Start: %v\n", err)
}
}
package db
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/cloudmock/config"
"github.com/cloudmock/secret"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
)
const ENV = "ENVIRONMENT"
func NewDatabaseConnection() *mongo.Collection {
var err error
log.Print("Connecting to mongodb")
conf, err := config.LoadConfigPath("config/app")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("")
}
env := os.Getenv(ENV)
var client *mongo.Client
conn, err := secret.GetSecrets()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("mongo db secret url failed %v", err)
}
if env == "dev" {
fmt.Println("Connecting to localdb")
client, err = mongo.NewClient(options.Client().SetAuth(
options.Credential{
Username: conf.DBuser,
Password: conf.DBpassword,
}).ApplyURI(conf.DBurl))
} else {
client, err = mongo.NewClient(options.Client().ApplyURI(conn))
}
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("mongo db client failed %v", err)
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 10*time.Second)
defer cancel()
err = client.Connect(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("mongo db connection failed %s", err) //nolint:gocritic
}
return client.Database("function").Collection("payments")
}
package router
import (
"encoding/json"
"github.com/brianvoe/gofakeit/v6"
"net/http"
)
type UserDetails struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Email string `json:"email"`
Phone string `json:"phone"`
Address string `json:"address"`
Company string `json:"company"`
JobTitle string `json:"jobTitle"`
}
func NewUserWrite() *[]UserDetails {
var usr []UserDetails
for i := 0; i < gofakeit.RandomInt([]int{5, 10, 12, 4, 11}); i++ {
usr = append(usr, UserDetails{
Name: gofakeit.Name(),
Email: gofakeit.Email(),
Phone: gofakeit.Phone(),
Address: gofakeit.Address().Address,
Company: gofakeit.Company(),
JobTitle: gofakeit.JobTitle(),
})
}
return &usr
}
func User() func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
jData, err := json.Marshal(NewUserWrite())
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Write(jData)
}
}
package p
import (
"github.com/cloudmock/router"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/v5"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/v5/middleware"
"github.com/go-chi/httprate"
"github.com/rs/cors"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func GoMock(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
rc := chi.NewRouter()
conn := db.NewDatabaseConnection()
rc.Use(middleware.RealIP)
rc.Use(middleware.Logger)
rc.Use(httprate.Limit(
2,
1*time.Second,
httprate.WithLimitHandler(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
http.Error(w, "too many requests", http.StatusTooManyRequests)
}),
))
rc.Route("/api/v1", func(rc chi.Router) {
rc.Get("/users", router.User())
rc.Get("/categories", router.Category())
})
cors.Default().Handler(rc).ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
Deploy cloud function
name: Build and Deploy to CloudFunction
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
deploy:
name: deploy
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@master
with:
project_id: ${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
service_account_key: ${{ secrets.gcp_credentials }}
export_default_credentials: true
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Deploy serverless function
run: |
gcloud functions deploy "GoMock" \
--runtime go113 --trigger-http \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--region australia-southeast1 \
--update-env-vars MONGODB=${{ secrets.mongo_secret }} \
--max-instances 2 \
--memory 128mb \
--service-account=${{ secrets.service_account }} \
--no-user-output-enabled
Why Mocking using cloud function
Use cases of mocking using cloud function
System Testing
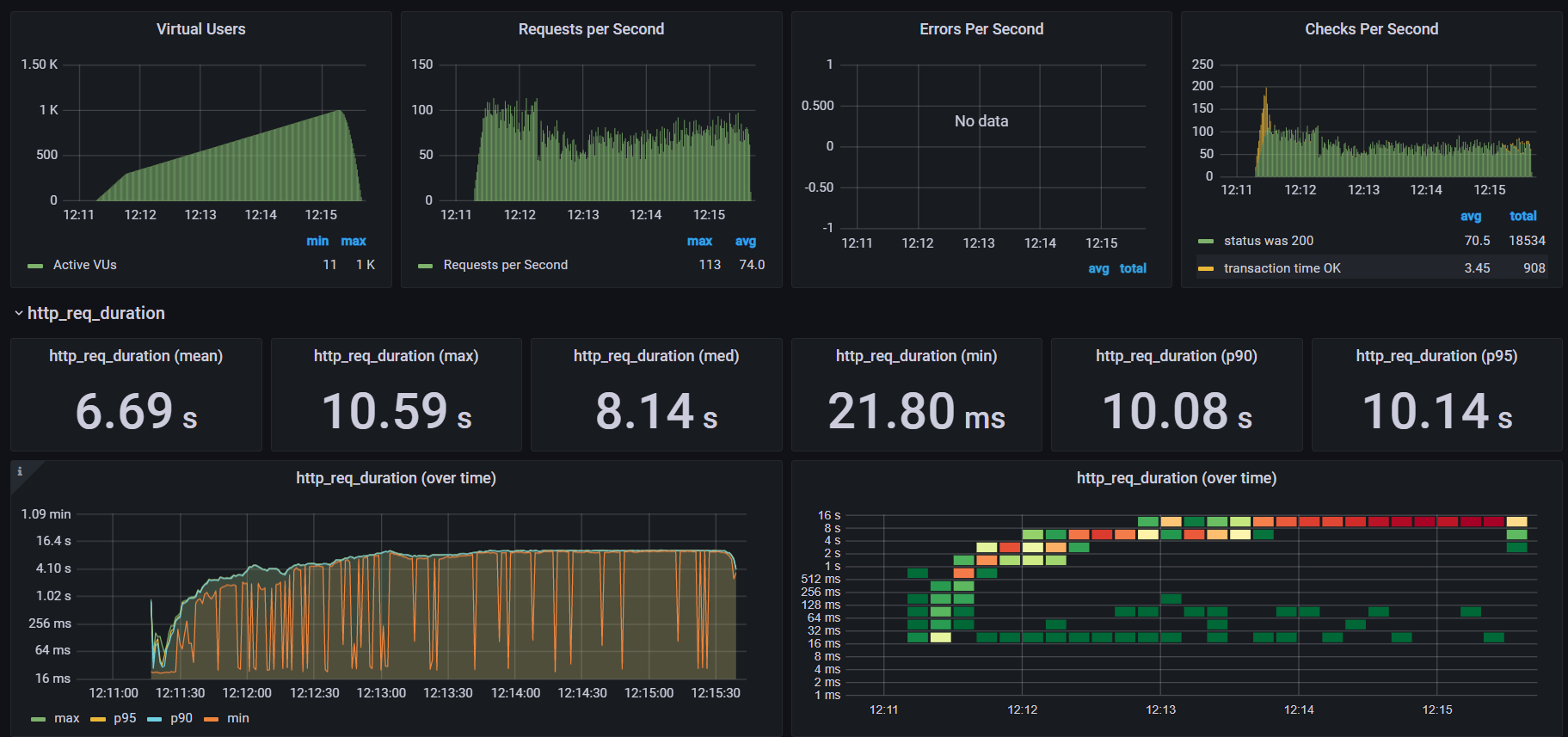
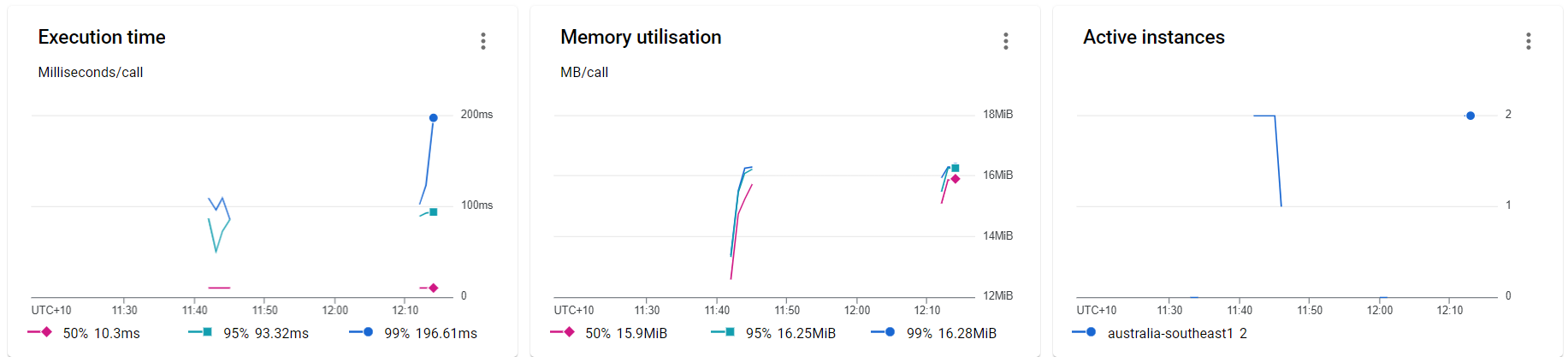
Performance testing
Performance tests check the behaviors of the system when it is under significant load. These tests are non-functional and can have the various form to understand the reliability, stability, and availability of the platform. For instance, it can be observing response times when executing a high number of requests, or seeing how the system behaves with a significant of data.